Serous Membrane That Lines The Abdominal Cavity. Find out everything you need to know about it here. The serous membrane allows for frictionless movement in a number of vital.
It is composed of mesothelial cells that are supported by a thin layer of fibrous tissue and is embryologically derived from the mesoderm. What is the name of the serous membrane that lines the organs? This membrane expands from the internal surface of the abdominal wall to completely or partially surround organs of the abdominopelvic cavities.
The Peritoneum Serves To Support The Organs Of The Abdomen And Acts As A Conduit For The P.
Also know, what is abdominal lining? The serous membrane, or serosal membrane, is a thin membrane that lines the internal body cavities and organs such as the heart, lungs, and abdominal cavity. The visceral peritoneum covers some of the organs in the abdominal cavity as well as some in the pelvic cavity.
Here’s The Serous Membrane That Lines The Abdominal Cavity, The Parietal Peritoneum.
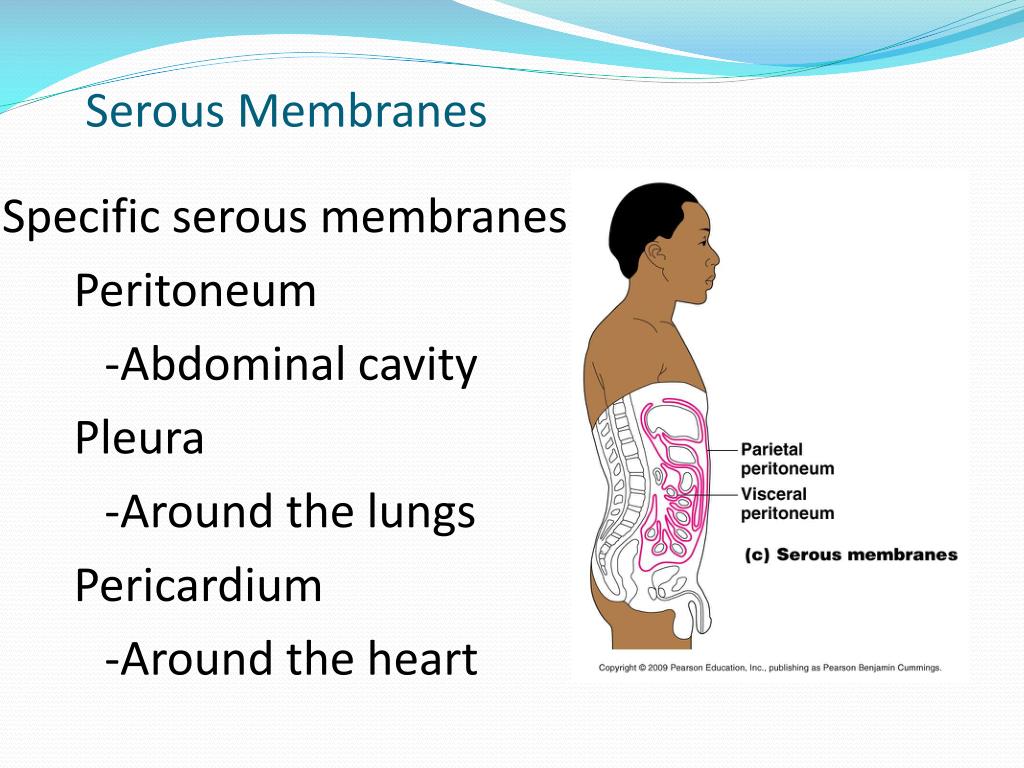
Membrane on the surface of the organs of the abdominal cavity (covers gut surface) visceral, pleura serous membrane, that lies closest, to the lung tissue parietal, peritoneum serous, membrane, that lies most superficial to the visceral organs in the abdominal cavity visceral, pericardium serous, membrane, that lies closest to the heart We’ll see it in more detail in volume six. What is the name of the serous membrane that lines the organs?
Find Out Everything You Need To Know About It Here.
The serous membrane, or serosal membrane, is a thin membrane that lines the internal body cavities and organs such as the heart, lungs, and abdominal cavity. Beneath the peritoneum there’s a continuous layer of loose connective tissue, here as we’ve seen it’s called the iliacus fascia. The peritoneum completely or partially lines the internal surface of the abdominal wall and organs of the abdominal cavity.
An Internal Visceral Layer Surrounds The Organs, While A Parietal Layer Forms The Walls Of The Body Cavities.
Here on the inside of the anterior abdominal wall it’s called the transversalis fascia This membrane expands from the internal surface of the abdominal wall to completely or partially surround organs of the abdominopelvic cavities. This can be seen in the lungs, with the pleural cavity.
The Peritoneum Serves To Support The Organs Of The Abdomen And Acts As A Conduit For The Passage Of Nerves, Blood Vessels, And Lymphatics.
The portion that covers the viscera and other intraabdominal structures is known as the visceral peritoneum, and that which lines the abdominal cavity is known as the parietal peritoneum. The serous membrane that lines the surfaces of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. It is composed of mesothelial cells that are supported by a thin layer of fibrous tissue and is embryologically derived from the mesoderm.
Related Posts
- Words That Start With AcroWords That Start With Acro. Root words, word roots, list of root words, root word acro, words with acro comments: Acrost — eye dialect of across.;acr ...
- A Room That Uses Numerous Columns To Support A Flat Ceiling Is Known As A HallA Room That Uses Numerous Columns To Support A Flat Ceiling Is Known As A Hall. The length of the beams is also a cost changer, because the longer th ...
- When Traveling At A Safe Speed On An Expressway Select A Lane That Allows Others ToWhen Traveling At A Safe Speed On An Expressway Select A Lane That Allows Others To. Adjust your speed or move into the center lane. If you are trave ...
- Parallel Construction Means ThatParallel Construction Means That. Parallel construction means that you a. Each paragraph of an essay begins the same way.PPT Parallel Construction Po ...
- Common Household Items That Weigh 500 GramsCommon Household Items That Weigh 500 Grams. Even closer when you add the box. 100ml of water weighs exactly 100 grams.12 Common Household Items That ...
- Is It Correct To Store Towels That Are Used To Clean Food Spills In A Sanitizer SolutionIs It Correct To Store Towels That Are Used To Clean Food Spills In A Sanitizer Solution. Cleaned and sanitized click again to see term 👆 1/39 previ ...
- Friedrich Hayek Believed ThatFriedrich Hayek Believed That. Hayek believed that when it came to money, milton friedman was still a keynesian, not on monetary theory but on method ...


